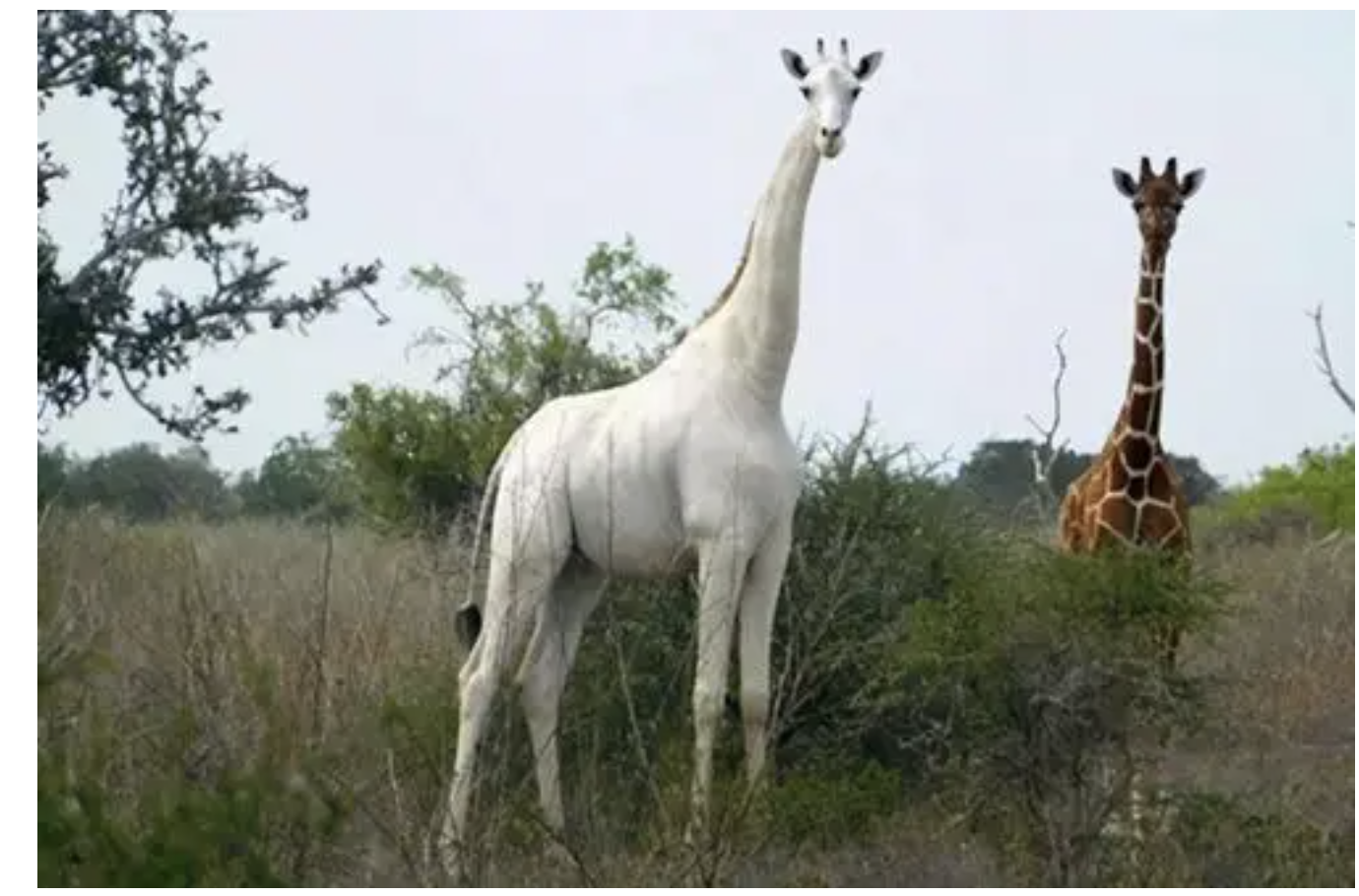
In the vast African land, Kenya is famous for its rich wildlife resources. Among them, giraffes, as a unique symbol of this land, have always attracted much attention. In order to better protect these elegant creatures, Kenya has taken an innovative measure to protect giraffes – using GPS tracker devices.
Giraffes are the tallest land animals in the world, and their unique appearance and gentle personality are deeply loved by people. However, with the continuous expansion of human activities, illegal hunting and habitat destruction, the survival of giraffes faces severe challenges. In this situation, Kenyan conservation agencies and researchers are actively seeking new ways to strengthen the protection of giraffes.
The introduction of GPS tracker devices has brought new hope for giraffe protection. This device can be installed on giraffes to monitor their movement trajectories in real time through satellite signals. With the help of professional software and equipment, researchers can track the location of giraffes at any time and understand their range of activities in different time periods.
By analyzing the movement trajectories of giraffes, researchers can better understand their habitat use. Giraffes move between different areas when looking for food, water sources and suitable resting places. GPS tracker devices can accurately record these movement paths, helping researchers determine areas where giraffes frequently move, so as to carry out targeted protection. For example, if a certain area is found to be where giraffes often forage, conservation agencies can take measures to strengthen protection of the area to prevent illegal hunting and interference from human activities.
At the same time, GPS tracker devices can also help researchers understand the migration patterns of giraffes. In different seasons, giraffes may migrate due to changes in food and water sources. By tracking their migration routes, researchers can make protection plans in advance to ensure that giraffes can safely pass through various potential dangerous areas during migration. For example, set up protection channels on the necessary routes for giraffe migration to prevent them from being affected by road construction and vehicle traffic.
In addition, GPS tracker devices also provide real-time monitoring methods for protection work. Once a giraffe shows abnormal conditions, such as staying in a certain place for a long time or deviating from the normal range of activities, researchers can respond quickly and send personnel to check the situation. This helps to promptly detect and deal with possible dangers that giraffes may face, such as injuries, diseases, or threats from illegal hunters.
Kenya also faces some challenges in using GPS devices to protect giraffes. First, installing and maintaining these devices requires professional technology and equipment, and it is also necessary to ensure that no harm is caused to the giraffe’s body. Second, data collection and analysis requires a lot of time and effort, as well as professional knowledge and skills. However, despite these challenges, Kenya’s conservation agencies and researchers are still determined to advance this work because they are well aware of the importance of GPS devices for giraffe protection.
In short, Kenya’s use of GPS devices has opened up new avenues for giraffe protection. By monitoring the movement of giraffes in real time and understanding their habitat use and migration patterns, Kenya can more effectively protect giraffes and their habitats. This move not only brings hope for the survival of giraffes, but also provides valuable experience for global wildlife conservation. I believe that with the joint efforts of Kenya and the international community, this beautiful creature, the giraffe, will be able to continue to walk gracefully on the land of Africa.